Fungi, Sponges and Cnidaria
1. chitin in cell walls
2. multicellular forms often contain multiple nuclei/cell in hyphae -tube-like structures
3. typically parasitic (living on live material) or saprophytic (living on dead material)
4. Some form sybioses, e.g. mycorrhizae (fungi with roots, increase surface area of roots), lichen (fungi with green or blue-green algae)
5. some are major plant pests - rusts, smut, ergot (carry enzyme that breaks down lignin)
6. some cause problems for humans - urinary tract infections, athlete's foot, histoplasmosis grows in lungs
7. some are beneficial - yeasts are used to make bread, beer, wine, many fungi are edible
B. Phylum Zygomycota - conjugation fungi: bread mold
1. haploid hyphae lack cell walls, represent dominant form
2. asexual reproduction occurs when hyphae produce sporangium, which produce spores
3. sexual reproduction involves fusion of gametes from 2 different mating types
4. neither spores nor isogamous gametes are motile
5. only diploid stage is the zygote, which gives rise to a fruiting body carrying haploid spores
C. Phylum Ascomycota - sac fungi: brewer's and baker's yeast, lichen, cottony mold, cup fungi, penicillin (life cycle is similar to slime molds)
1. produce ascus during sexual cycle - a sac with 8 haploid spores
2. sexual reproduction occurs when hyphae from opposite mating types touch
3. hyphae grow together to produce fruiting body, +/- hyphae produce zygotes
4. zygote undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid cells, which then divide mitotically to produce 8 ascospores
5. asexual reproduction occurs through conidia, which bear conidia spores
6. lichens represent obligate associations between fungi and green algae or blue-green algae
D. Phylum Basidiomycota - club fungi, includes mushrooms, puffballs, bracket fungi, rusts, smut
1. above ground structure is composed of dicaryotic (2 nuclei/cell) hyphae formed after hyphal union
2. nuclei fuse in some hyphae, then undergo meiosis to produce 4 spores
3. Structure containing spores is a club-shaped basidia
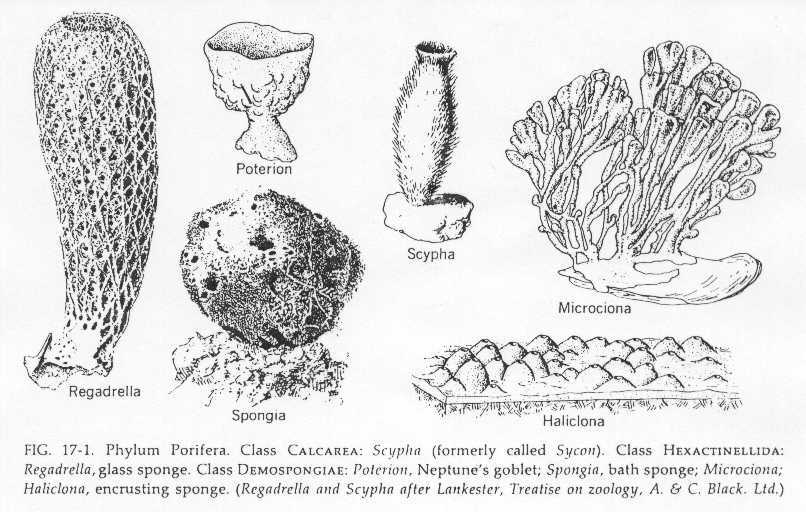
II. Phylum Porifera: Sponges - (Kingdom Animalia, subkingdom Parazoa)

A. Features
1. larvae are ciliated and free-swimming
2. adults are sessile (attached to substrate) and diploid
3. most are a simple tube with
a. outer epidermal cells
b. middle layer of amoeboid cells
c. inner layer of choanocytes (collar cells) with flagella which move water out of the mouth of the sponge
4. internal skeleton made of
a. crystalline spicules - either silica or calcium carbonate
b. or proteinaceous fibers (bath sponge is an example of a sponge skeleton)
B. Some sponges can be dissassociated into cells and will reform into a sponge
C. Asexually reproduce by budding
D. Also can sexually reproduce
1. eggs and sperm are formed in collar cells
2. sperm swim to eggs, effect fertilization to form a zygote
3. zygote undergoes mitosis to form multicellular blastula with cilia
4. the blastula disperses by swimming, then invaginates and settles on the substrate to form a new sponge.

III Section Radiata (Kingdom Animalia, subkingdom Eumetazoa)
A. Features
1. radial symmetry - body parts arranged around a central axis
2. digestive cavity with one opening: mouth = anus
3. bodies have 3 layers of cells: inner, outer and middle w/unspecialized amoeboid cells
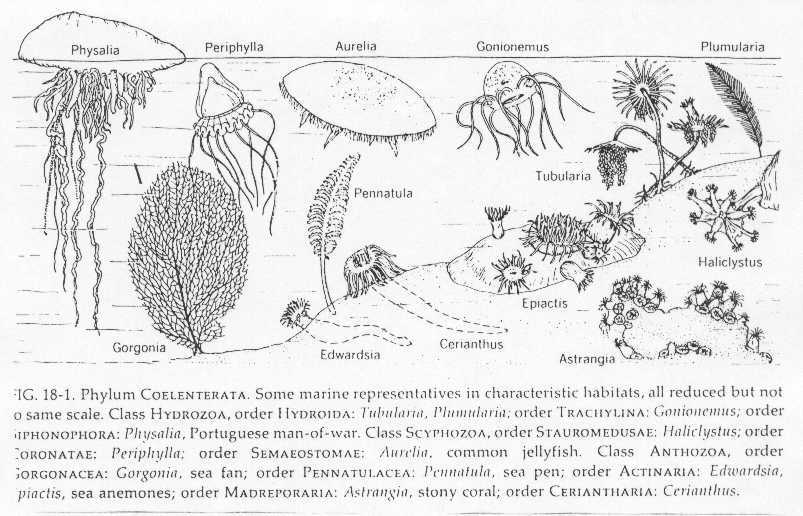
B. Phylum Cnidaria (also known as coelenterates)
1. outer epidermis contains 5 cell types
a. sensory-nerve cells
b. gland cells
c. nematocyst cells - which inject nerve toxins
d. muscle cells
e. interstitial cells
2. Class Hydrozoa - solitary (hydra) and colonial forms

a. dominant form is diploid polyp
b. colonial species alternate polyp with small male or female medusa stage
c. motile sperm fuse with planktonic eggs to form zygotes
d. zygotes go through mitotic divisions to produce blastula
e. blastula produces a planula larvae
f. planula settles and grows into a new polyp colony, which reproduces asexually
3. Class Scyphozoa - jellyfish
a. dominant form is diploid polyp which alternates with large male or female medusa
b. medusas use nematocysts on stinging tentacles to capture prey
c. motile sperm fuse with planktonic eggs to form zygotes
d. zygotes go through mitotic divisions to produce blastula
e. blastula produces a planula larvae
f. planula settles and grows into a new polyp which reproduces asexually
4. Class Anthozoa - corals, sea anemones, sea fans
a. lack medusa stage, have more complicated guts with walls
b. corals secrete calcium carbonate shells that become coral reefs
c. corals represent symbiotic associations between photosynthetic dinoflagellate zooxanthellae and anthozoan polyps

B. Phylum Ctenophora - comb jellies or sea walnuts
1. 8 rows of cilia around body, transparent
2. marine, float, lack nematocysts
3. have separate mouth and anus
4. common in lower Chesapeake